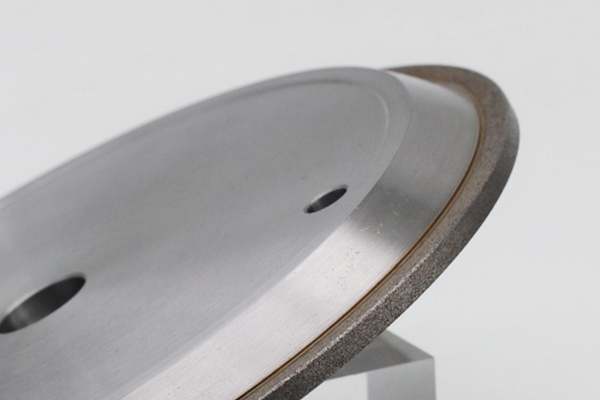
Why Metal CBN Grinding Wheels Can Efficiently Machining 4Cr13 White Iron
4Cr13 martensitic stainless steel, with its excellent corrosion resistance and heat-treatable strengthening properties, is widely used in white iron processing for manufacturing high-hardness, wear-resistant precision components such as precision cutting tools, valve parts, and medical device components. When the material hardness reaches around 53HRC, its comprehensive performance achieves an optimal balance between processability and practical application demands. However, this high hardness also presents significant machining challenges. Metal CBN grinding wheels, with their superior performance, are an ideal choice for machining 53HRC 4Cr13 white iron.

4Cr13 white iron
4Cr13 White Iron: Material Characteristics and Machining Challenges at 53HRC Hardness
4Cr13 Material Characteristics and Advantages at 53HRC Hardness
4Cr13 steel contains approximately 0.36%~0.45% carbon and 12%~14% chromium. After quenching and low-temperature tempering, its hardness can stably reach around 53HRC. In this hardness range, the material’s wear resistance significantly improves, effectively resisting impact and friction wear during machining. Simultaneously, it retains good toughness, avoiding the risk of brittle fracture that might occur with excessively high hardness (e.g., above 58HRC).
In white iron processing applications, 53HRC 4Cr13 components are suitable for working conditions involving corrosive media or frequent friction, such as conveying parts in food processing machinery or valve cores in chemical pipelines. Its corrosion resistance effectively slows down surface oxidation and rusting, while the moderate hardness ensures component service life and operational stability.
Core Challenges of Machining 53HRC 4Cr13 White Iron
Traditional machining methods face multiple challenges when dealing with 4Cr13 white iron at 53HRC hardness:
High Cutting Resistance and Rapid Tool Wear: The high hardness leads to a sharp increase in plastic deformation resistance during cutting. Tool edges experience significantly higher impact loads and thermal loads. This causes common tools to chip easily, wear out quickly, and struggle to maintain stable machining accuracy.
Significant Work Hardening Phenomenon: During cutting, the surface metal of 4Cr13 undergoes plastic deformation, resulting in work hardening. The hardened layer’s hardness can be 1.5 to 2 times that of the base material, further exacerbating tool wear and machining difficulty in subsequent cutting operations.
High Thermal Sensitivity, Prone to Affecting Performance: Martensitic stainless steel has poor thermal conductivity. Cutting heat tends to concentrate in the tool-workpiece contact area. If cooling is insufficient, localized overheating of the workpiece can lead to temper softening, compromising the desired 53HRC hardness and significantly reducing tool life.
Metal CBN Grinding Wheels: The Sharp Tool to Conquer 53HRC 4Cr13 White Iron Machining Difficulties
To overcome the aforementioned machining challenges, using high-performance abrasives is crucial. Metal CBN grinding wheels, with their superior performance, are an ideal choice for machining 53HRC 4Cr13 white iron. According to customer feedback, our company’s metal CBN grinding wheel products have successfully resolved customer issues in processing 53HRC 4Cr13 white iron and have led to repeat purchases, fully demonstrating their efficiency and reliability.
The advantages of metal CBN grinding wheels include:
* Ultra-High Hardness and Wear Resistance: CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride), one of the hardest known materials, is second only to diamond in hardness. Metal bond CBN grinding wheels possess excellent wear resistance, effectively counteracting the extremely high cutting resistance of 53HRC 4Cr13 steel. This significantly reduces grinding wheel chipping and wear, ensuring grinding stability and machining accuracy.
* Exceptional Thermal Conductivity: Compared to traditional abrasives, CBN has better thermal conductivity. This helps to rapidly dissipate heat generated in the grinding zone, effectively preventing workpiece temper softening due to localized overheating, ensuring the workpiece hardness remains at 53HRC, and extending the grinding wheel’s lifespan.
* Effective Work Hardening Suppression: The sharp abrasive grains and stable grinding performance of metal CBN grinding wheels effectively reduce plastic deformation on the workpiece surface, thereby suppressing the formation of work-hardened layers and lowering the difficulty of subsequent grinding.
* Maintenance of Form and Dimensional Accuracy: The metal bond imparts excellent form retention to CBN grinding wheels, allowing them to maintain their original geometry during prolonged grinding. This ensures that machined workpieces achieve high dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
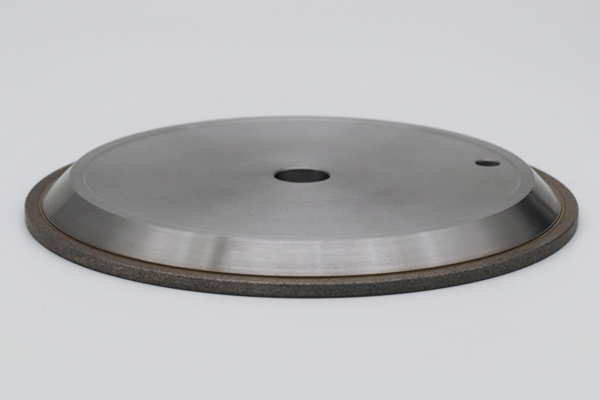

Optimizing the Process to Maximize the Efficacy of Metal CBN Grinding Wheels
Combining the characteristics of metal CBN grinding wheels, the following process optimization strategies will further enhance the machining efficiency and quality of 53HRC 4Cr13 white iron:
* Precise Heat Treatment for Hardness Control: Pre-treating the 4Cr13 blank with quenching and low-temperature tempering is essential. Quenching temperature should be controlled at 10501070℃, followed by oil cooling after holding; tempering temperature at 150200℃, held for 23 hours, to ensure the final hardness is stably within the 5254HRC range, providing a consistent material basis for subsequent grinding.
* Efficient Cooling and Lubrication: During grinding, extreme pressure emulsion or specialized stainless steel cutting oil should be used, with high-pressure cooling. Directing the cutting fluid to the grinding wheel-workpiece contact area promptly dissipates heat, reduces grinding wheel and workpiece temperatures, and minimizes friction, further inhibiting work hardening.
Quality Control and Common Problem Solving:
* Hardness Consistency Testing: Multi-point testing of the workpiece with a Rockwell hardness tester before and after machining is necessary to ensure hardness values are within ±1 HRC of 53HRC.
* Common Issues and Countermeasures:
* Grinding Wheel Chipping: Check if grinding parameters are reasonable, ensure the grinding wheel is sharp, and consider optimizing the grinding wheel bond or grit size.
* Excessive Workpiece Surface Roughness: Optimize fine grinding parameters, select finer grit CBN grinding wheels, and enhance cooling and lubrication.
* Workpiece Deformation After Machining: Reduce single grinding depth, add a stress-relief annealing step, and optimize clamping methods with fixtures to reduce clamping stress.
Conclusion
Facing the challenges of machining 53HRC 4Cr13 white iron, metal CBN grinding wheels, with their unique properties of ultra-hardness, wear resistance, and high thermal conductivity, are key to achieving efficient and precise processing. Choosing the right metal CBN grinding wheels and combining them with optimized process flows will not only significantly improve machining efficiency and ensure product quality but also bring long-term competitive advantages to your enterprise.