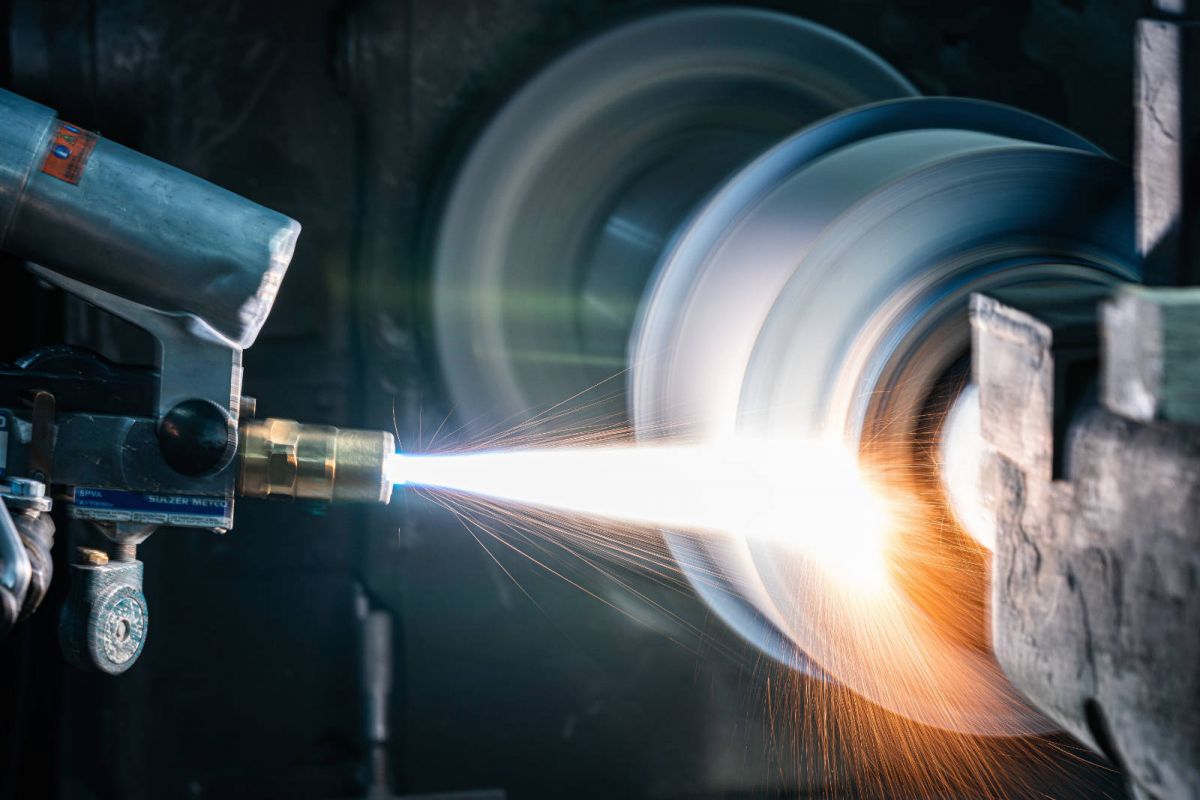
Resin Diamond Grinding Wheel for Tungsten Carbide and Laser-Cladded Stellite-6 Layer
Resin bond diamond grinding wheels are widely used in precision industries for machining ultra-hard materials such as tungsten carbide (WC). In recent years, with the growing application of laser cladding and thermal spray coatings, more attention has been drawn to the grinding of hardfacing layers like Stellite-6. These two materials — WC coatings and Stellite-6 overlays — share high hardness and wear resistance, but their grinding behavior differs significantly.
Introduction: Why grinding these materials matters
With the development of wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant surface engineering, tungsten carbide coatings and Stellite-6 laser cladding layers are increasingly used in industries such as automotive, energy, oil and gas, aerospace, and tooling.
These coatings improve component lifespan, reduce friction, and protect parts from wear and corrosion. However, because of their extreme hardness (HV > 1000) and tough matrix structure, they are notoriously difficult to machine after coating.
Grinding is often the final step for achieving the desired surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and geometric precision. Selecting the proper superabrasive grinding wheel is the key to success.
Material Overview
Tungsten Carbide (WC) Coating
Tungsten carbide coatings are typically deposited by HVOF (High Velocity Oxy-Fuel) or plasma spray processes.
These coatings consist of hard WC particles embedded in a metallic binder such as cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), or chromium (Cr).
Key characteristics:
* Hardness: 1200–1800 HV
* High wear resistance and low friction
* Brittle structure (can crack if overloaded)
* Chemically compatible with diamond — diamond is the best abrasive for WC
Grinding challenges:
* Brittle microstructure → risk of micro-cracking if too aggressive
* High hardness → high grinding force and heat
* Porosity and coating bond line → risk of edge chipping or delamination
Stellite-6 (Laser Cladding Layer)
Stellite-6 is a cobalt-based hardfacing alloy composed mainly of Co, Cr, and W with dispersed carbides (Cr₇C₃, WC, etc.).
When applied by laser cladding, the layer becomes dense, metallurgically bonded, and exhibits minimal dilution with the substrate.
Typical properties:
* Hardness: 450–600 HV (matrix) + 1000–1200 HV (carbides)
* Excellent wear, corrosion, and heat resistance
* Tough and ductile matrix supports embedded carbides
Grinding challenges:
* The cobalt matrix reacts chemically with diamond at elevated temperatures, causing graphitization and rapid wear of diamond grains.
* The mixed microstructure (soft matrix + hard carbides) leads to uneven grinding loads.
* The layer can work-harden under mechanical stress or excessive heat.
Therefore, while diamond wheels are ideal for tungsten carbide, they are not suitable for Stellite-6. For Stellite-6 and other cobalt-based materials, CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) grinding wheels are the better choice.
How to Grind Tungsten Carbide Coating
Wheel selection
Recommended wheel:
Resin bond diamond grinding wheel
Reasons:
The resin bond offers good self-sharpening behavior — when the bond wears, new diamond grains are exposed.
* It provides a flexible cutting action and minimizes brittle fracture.
* Suitable for both rough grinding and precision finishing of WC coatings.
Suggested specification example:
* Abrasive: Synthetic diamond
* Bond: Resin (phenolic, hybrid, or copper-resin)
* Grit size: 120#–400# (depending on roughness requirement)
* Concentration: 75%–100%
* Hardness: Medium
* Wheel shape: 1A1, 6A2, 11V9, or cup wheel depending on part geometry
Grinding process parameters
* Wheel speed: 20–35 m/s
* Feed rate: 0.01–0.03 mm per pass for finishing
* Depth of cut: 0.005–0.02 mm
* Coolant: Emulsion or synthetic coolant with continuous, abundant flow
* Dressing: Use silicon carbide stick or diamond dresser periodically to refresh cutting surface
Tips for WC coating grinding
* Avoid excessive heat — overheating may cause cobalt leaching or surface oxidation.
* Steady coolant flow is essential — intermittent coolant causes thermal shock and cracking.
* Use a sharp wheel — dull diamonds cause rubbing and burning.
* Use light pressure for finishing to achieve mirror-like surface (Ra < 0.1 μm).
* Check adhesion layer — if coating is thin or poorly bonded, avoid heavy roughing.
Grind Stellite-6 (Laser Cladding) Layer
Why not diamond?
Stellite-6 is cobalt-based, and cobalt dissolves carbon from diamond at grinding temperatures (>700°C), forming graphite. This results in:
* Rapid diamond wear
* Loss of sharpness
* Wheel glazing and surface burn
Therefore, diamond wheels are not recommended for continuous grinding of Stellite-6. Instead, CBN should be used.
Recommended wheel type
Resin bond CBN grinding wheel
Advantages:
* Chemical stability with ferrous and cobalt alloys
* Good surface finish capability
* Low grinding force and temperature
* Elastic bond structure helps reduce vibration and chatter
Specification example:
* Abrasive: CBN (C100 or C125 grade)
* Bond: Resin or hybrid resin bond
* Grit size: 100#–240# for finishing
* Concentration: 75%–100%
* Hardness: Medium-soft
* Wheel speed: 25–35 m/s
Grinding process for Stellite-6
Use abundant coolant — oil-based or water-soluble synthetic coolant to minimize temperature rise.
Set moderate wheel speed — too high speed causes matrix smearing or work-hardening.
Use light feed and multiple passes — reduces thermal load and improves accuracy.
Dress regularly with diamond stick (fine grit) to maintain open cutting surface.
Avoid mechanical shocks — Stellite can chip or crack near the bond line.
Typical parameters (starting point):
* Depth of cut: 0.005–0.02 mm
* Feed rate: 0.01–0.05 mm/s
* Traverse speed: 3–5 m/min
For machining the Laser Stellite 6 layer, Moresuperhard will create two formulas: one using only the CBN and the other mixing diamond and CBN material for customer testing. We are waiting for the update…
Recently Moresuperhard received customer inquiry about carbide coating and Laser-Cladded Stellite-6 Layer, lets see it together:
Case of Resin bond diamond grinding wheel for carbide coating
| Resin bond diamond grinding wheel for carbide coating and Laser Stellite 6 layer | |
| Customers need | 1A1 D19x7x7 D181 |
| 1A1 D300xH127xT32xX10 D181 | |
|
Sugesstions
|
1/ 1A1 D200 x 32 x 20×10 #181. Qty: 02 pcs (for machining the Laser Stellite 6 layer)
2/ 1A1 D200 x 32 x 20×10 #181. Qty: 02 pcs (for machining Carbide) 3/ 1A1 D200 x 32 x 20×10 #250. Qty: 02 pcs (for machining Carbide) |