Case of metal CBN cutting disc for cutting automobile valve stem
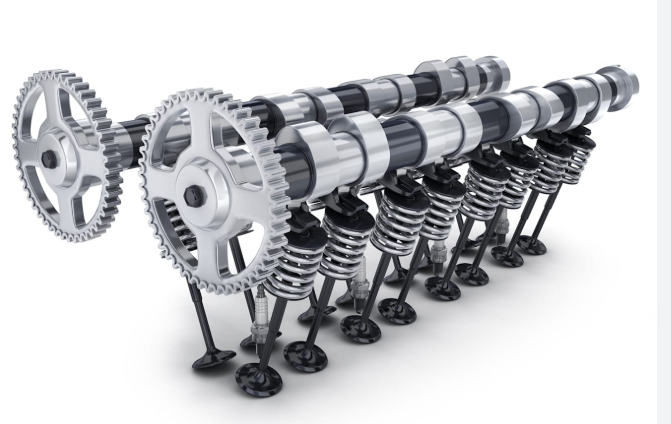
What is an Automobile Valve?
In the internal combustion engine, the automobile valve plays a crucial role in the process of fuel combustion and exhaust emission. It regulates the intake of air-fuel mixture into the combustion chamber and the exhaust of gases after combustion. Typically, there are two types of valves in a four-stroke engine: the intake valve and the exhaust valve.
Each valve is composed of two main parts:
* Valve head – the disc that seals against the valve seat in the cylinder head.
* Valve stem – the long rod that connects to the camshaft or rocker arm and transmits motion to open or close the valve.
The valve stem is especially critical in ensuring accurate operation and durability. It must withstand high temperatures, friction, and corrosive gases, while maintaining tight tolerances and smooth finishes. To achieve this, manufacturers use high-strength alloys and precision grinding methods, where CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) grinding wheels are increasingly becoming the go-to choice.
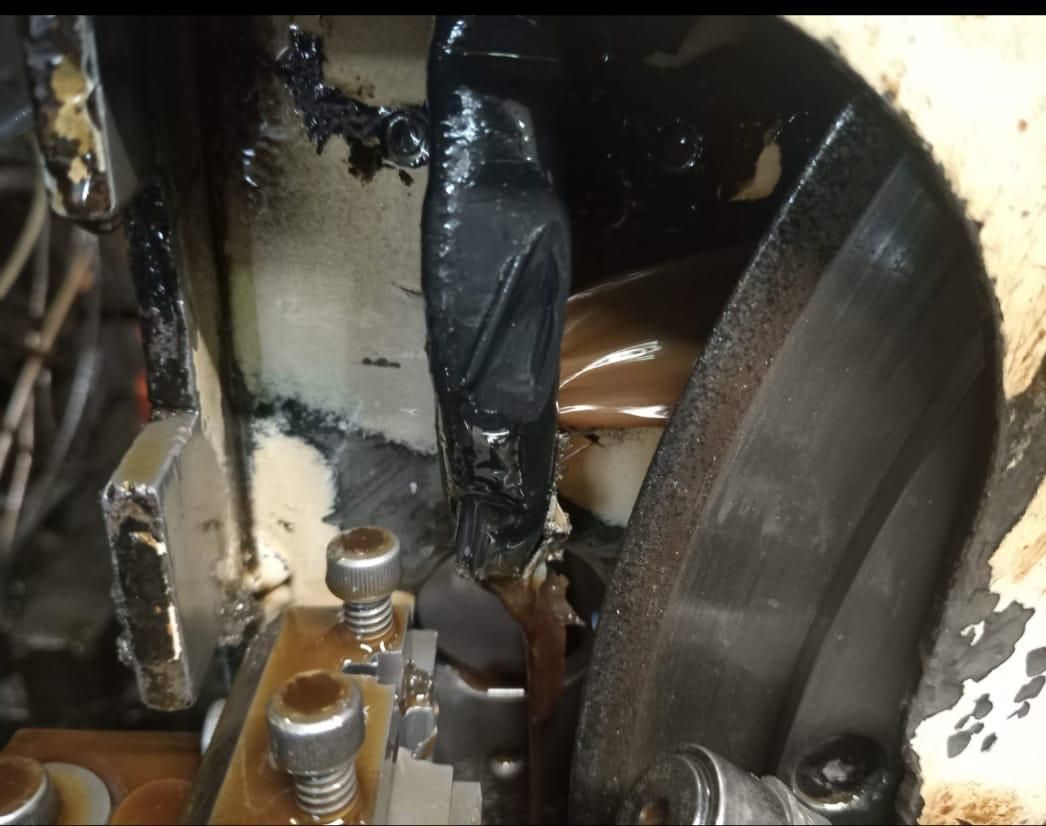
Cutting the valve stem is one of the key steps in the valve manufacturing process. It typically takes place after hot forging or rough machining, where the forged stem is trimmed to precise length before grinding. The choice of cutting disc is critical to ensure a clean, burr-free cut, minimize material waste, and avoid thermal damage (e.g., burning or deformation).
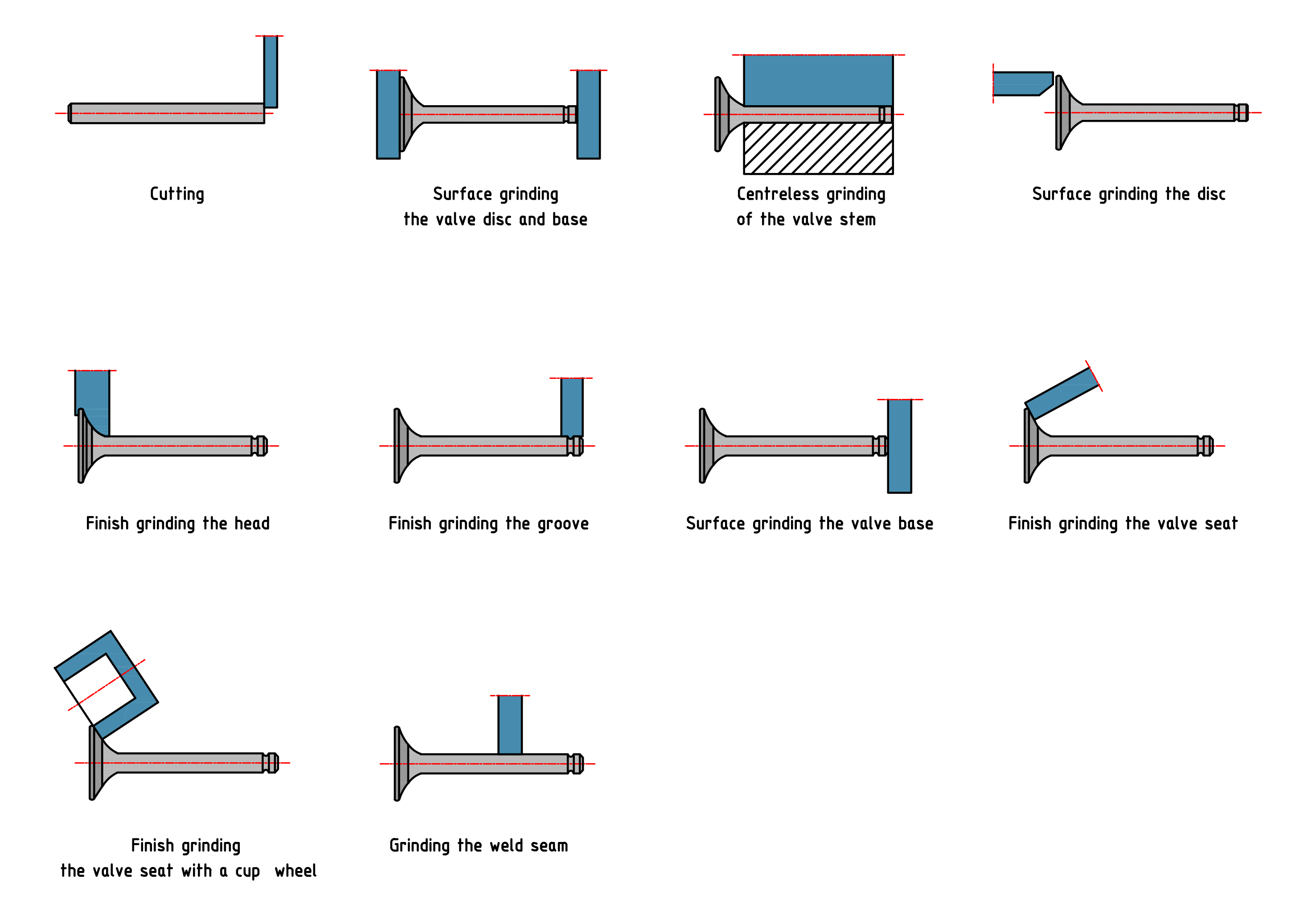
Manufacturing Process of Automobile Valve
The production of automobile valves involves several key steps to ensure performance, precision, and reliability. The stem requires fine surface finishes, accurate diameters, and defect-free structure to function flawlessly in high-speed, high-temperature environments.
Step-by-Step Manufacturing Process:
Material Selection:
* Common materials include heat-resistant steel alloys such as SUH35, EN52, or Inconel for exhaust valves, and chromium-silicon steel for intake valves.
* The material must have good wear resistance, thermal fatigue resistance, and strength.
Hot Forging:
-
-
The blank is heated to high temperatures and forged into a rough valve shape.
-
Forging improves grain structure, strength, and toughness.
-
Heat Treatment:
-
-
-
Processes like normalizing, hardening, and tempering improve mechanical properties.
-
Induction hardening may be applied selectively to the stem to increase wear resistance.
-
-
Rough Machining:
-
-
Lathe operations shape the valve stem and head to rough dimensions.
-
Grooves and chamfers may be added.
-
Cutting Process:
Key Requirements for Cutting Valve Stems
* High precision to maintain exact stem length
* Fast cutting speed for productivity
* Minimal burr formation to reduce post-processing
* Durability to handle tough alloys like Inconel, SUH35, or chrome-silicon steel
* Cool cutting to prevent thermal damage
Resin Bond CBN Cutting Disc
* Advantages:
-
-
Sharp cutting edge
-
Lower cutting resistance
-
Good for high-speed cutting
-
* Best For:
Metal Bond CBN Cutting Disc
* Advantages:
-
-
-
Much longer tool life
-
Maintains shape and cutting edge over long runs
-
Ideal for automation and high-precision production
-
-
* Best For:
-
-
-
-
Large-volume production lines
-
Hard valve materials (Inconel, martensitic steel)
-
Situations requiring minimal dressing and high dimensional control
-
-
-
Grinding Process:
-
-
The stem surface is ground to precise dimensions and finishes using centerless grinding.
-
CBN grinding wheels, particularly metal-bonded types, are used to maintain high accuracy and tool life.
-
Surface Treatment:
-
-
Chrome plating, nitriding, or phosphating may be applied to improve wear resistance and reduce friction.
-
Inspection:
-
-
Dimensional checks, surface roughness measurement, and hardness testing are conducted.
-
Automated visual inspection systems may detect surface defects.
-
How to choose a cutting disc for cutting automobile valve stem?
Before grinding, cutting or parting off operations are needed to trim or separate the forged valve blank. Choosing the right cutting disc is crucial for clean cuts and avoiding damage to the stem.
Key Factors in Choosing a Cutting Disc:
| Parameter | Recommended Choice |
| Material Compatibility | Use discs suitable for heat-resistant steel and alloys
Resin bond or metal bond depending on required finish and rigidity |
| Disc Bond Type | |
| Abrasive Type | CBN for ferrous metals, Diamond for non-ferrous |
| Disc Hardness | Medium-hard to hard, depending on the valve blank hardness |
| Disc Thickness | Thin discs (1.0–2.0 mm) for minimal material loss |
| Cooling System | Always use coolant to reduce heat and extend tool life |
Recommended cutting disc:
For valve stem cutting, resin-bonded CBN cutting discs offer good performance due to their sharpness and fast cutting speed. However, for tougher materials or automated production lines, metal-bonded CBN discs offer better durability and consistency.
Advantages of metal CBN cutting disc for cutting valve stem
Metal-bonded CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) grinding wheels are widely adopted in valve manufacturing because of their exceptional performance on hard-to-grind ferrous materials. Compared to conventional abrasives (e.g., alumina) or even resin-bonded wheels, metal CBN wheels deliver superior precision, durability, and surface quality results.
1. High Grinding Efficiency:
-
CBN has a hardness second only to diamond and is ideal for hard steel and alloys.
-
Maintains sharp cutting edges over long periods, reducing downtime.
2. Excellent Surface Finish:
-
Achieves Ra < 0.2 µm surface roughness on valve stems.
-
Reduces friction and wear inside the engine valve guide.
3. Dimensional Accuracy and Stability:
-
Metal bond ensures high rigidity and form retention.
-
Perfect for high-precision centerless grinding of stems with tolerances of ±0.001 mm.
4. Longer Wheel Life:
-
Metal bond matrix resists wear and maintains grit sharpness.
-
Reduces frequency of dressing and wheel changes.
5. Thermal Stability:
-
Better heat resistance than resin bonds.
-
Suitable for dry grinding or minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) systems.
6. Cost-Effective for Mass Production:
-
Though initially more expensive, longer life and lower maintenance result in lower cost per piece in high-volume production.
Recent Case Study: CBN Grinding Wheel Application in Valve Stem Production
Client Profile:
Customer are looking for a possible supplier for one cBN cut-off wheel, please see the characteristics below:
| Workpiece | Automobile valve | O.D. | 380 mm |
| Thickness | 1.5 mm | ||
| The cutting life of the cBN should be 7 mm, as the print says. | |||
| Cutting wheel size | D400*T2mm | ||
| Competitor | The SUN company tried some samples, but they did not perform as the NORITAKE wheel. Customer tried with CDT and the first ones worked very wheel but then they could not make more wheels. | ||
| Customer feedback | Customer starts to test the CBN cut off wheel last week and looks like the wheel is doing well so far. The wearing is very little. So far today Friday, the wheel is 200k cycles, looks well. | ||
—-EDITOR: Doris Hu, Alan Wang
—-POST: Doris Hu