Good Feedback of Metal CBN Segment for Grinding Brake Disc
In the modern automotive industry, safety and performance are paramount. Among the many components that ensure a vehicle’s reliability, the brake disc (also called a brake rotor) plays a critical role. As a core part of the disc brake system, the brake disc is directly responsible for converting kinetic energy into thermal energy through friction. This ensures the vehicle can decelerate and stop safely.
Due to continuous usage, brake discs require precise machining and grinding to meet surface finish requirements, flatness tolerances, and dimensional accuracy. Grinding is one of the most important finishing processes in brake disc manufacturing, and selecting the right abrasive tools has a direct impact on both production efficiency and product quality.
In recent years, metal-bonded CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) grinding segments have emerged as one of the most reliable and effective tools for brake disc grinding. Customers worldwide have provided excellent feedback, praising their durability, precision, and efficiency compared with conventional abrasives.
This article will explore brake disc basics, explain how they are ground, introduce metal CBN segments, and highlight their advantages in brake disc grinding.
What is a Brake Disc?
A brake disc is a round, flat component attached to a vehicle’s wheel hub. When the driver applies the brake, the brake pads clamp onto the disc, generating friction to slow down or stop the wheel’s rotation.
Key characteristics of brake discs:
-
Material: Typically made of cast iron, sometimes reinforced with carbon composites or ceramics for high-performance vehicles.
-
Design:
-
Solid brake discs – simple and cost-effective, commonly used in standard passenger cars.
-
Ventilated brake discs – feature internal vanes to improve cooling, widely used in performance and heavy-duty vehicles.
-
-
Surface requirements: Brake discs must have:
-
Flatness and parallelism for even braking force.
-
Correct roughness to balance friction and wear.
-
Resistance to thermal stress and cracking.
-
Because of these requirements, grinding becomes a key process after casting and machining.
How to Grind Brake Discs?
Brake disc grinding is performed to achieve precise surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and ensure long-term braking performance.
Grinding Process Steps:
-
Pre-machining: After casting, brake discs undergo turning or milling to remove bulk material.
-
Rough grinding: Using large abrasive wheels to quickly remove excess material.
-
Fine grinding: Achieves the required thickness and surface precision.
-
Finishing / Lapping: Provides the final smooth surface to ensure proper brake pad contact.
Key requirements in grinding brake discs:
-
High efficiency: Automotive production requires high throughput.
-
Consistency: Every disc must meet tight tolerance levels.
-
Tool life: Grinding wheels or segments must withstand long operation cycles.
Traditional abrasives (aluminum oxide or silicon carbide) often fail to meet modern automotive production demands due to fast wear, frequent dressing, and inconsistent performance.
This is where CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) grinding segments come into play.
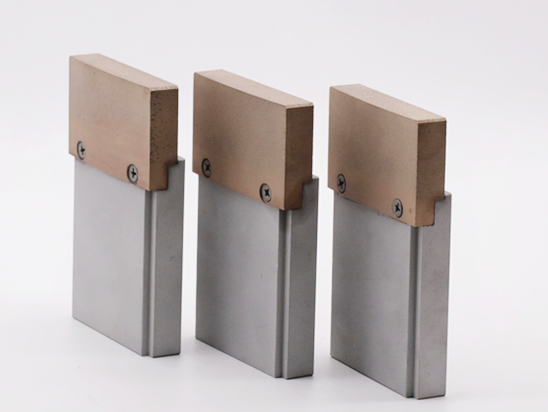
What is a Metal CBN Segment?
CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) is the second hardest material known, after diamond. However, unlike diamond, CBN is chemically stable when grinding ferrous materials like cast iron, making it the ideal abrasive for brake disc grinding.
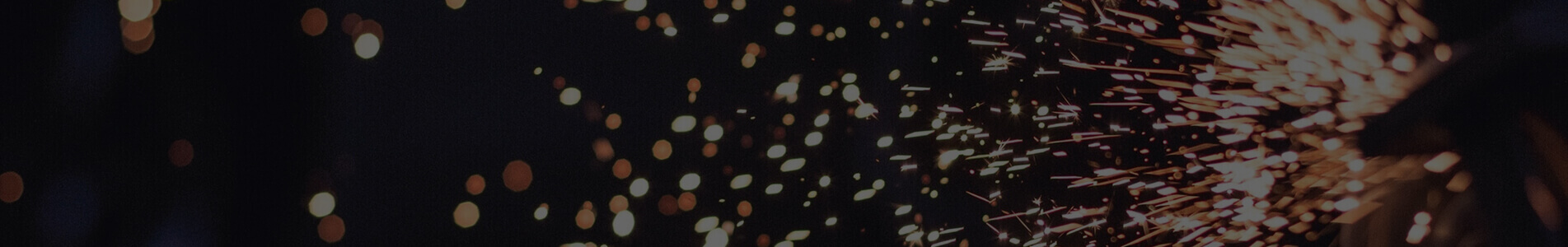
A metal CBN segment is a small block of metal-bonded CBN abrasives, typically mounted on a large grinding wheel or segmental wheel system.
Structure of metal CBN segments:
-
Abrasive: CBN particles, providing extreme hardness and cutting ability.
-
Bond: Metal bond matrix, ensuring strong holding power and excellent heat resistance.
-
Segment shape: Designed to cover grinding surface areas while allowing cooling fluid flow.
Applications of metal CBN segment:
-
Brake disc grinding (cast iron, carbon composite).
-
Brake drum grinding.
-
Automotive and railway braking system components.
Advantages of Metal CBN Segments for Grinding Brake Discs
Customer feedback has highlighted many advantages of metal CBN segments compared with conventional abrasives:
1. Superior Grinding Efficiency
-
CBN abrasives cut cast iron much faster than conventional abrasives.
-
Metal bond ensures consistent cutting edges are maintained for long periods.
-
This results in higher productivity and shorter cycle times.
2. Long Tool Life
-
Traditional abrasives wear out quickly, requiring frequent replacement.
-
Metal-bonded CBN segments last 5–10 times longer, reducing downtime.
-
Lower overall tool consumption reduces costs.
3. Stable Performance
-
Metal bond holds abrasive grains firmly, preventing premature grain loss.
-
Delivers consistent grinding results across thousands of brake discs.
4. Improved Surface Quality
-
CBN provides precise cutting, minimizing micro-cracks and thermal damage.
-
Brake discs ground with CBN segments show smoother surfaces and better flatness.
-
Results in quieter braking and longer brake pad life.
5. Heat Resistance
-
Grinding generates heat, especially with cast iron.
-
Metal CBN segments dissipate heat efficiently, preventing burn marks or warping.
6. Reduced Dressing Frequency
-
Conventional abrasives need frequent dressing to restore cutting ability.
-
CBN segments maintain their sharpness longer, requiring much less dressing.
-
Saves time and reduces production interruptions.
7. Cost-effectiveness in Mass Production
-
Although the initial cost of CBN segments is higher, the overall cost per brake disc is significantly reduced due to longer life and higher efficiency.
-
Ideal for large-scale automotive manufacturers.
Real Customer Feedback
| Inspect result | Metal CBN segment 160# |
| Workpiece material | FCD250 |
| Quantity | 24pcs/half- group 48pcs/hole-group |
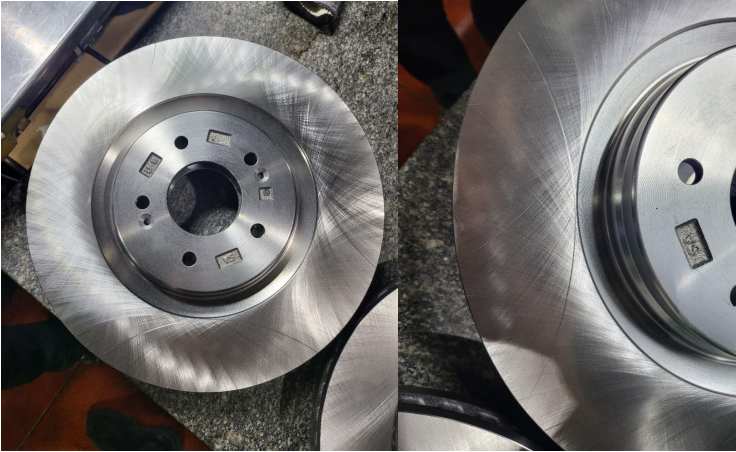
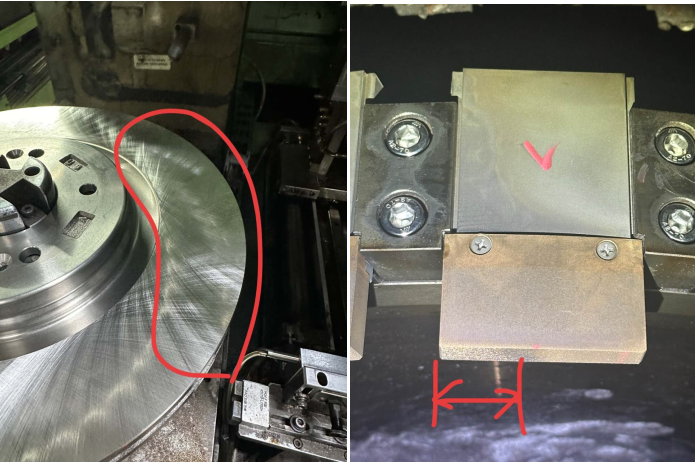
| Customer Request | The brake disc surface should have the same texture as in the image after machining. |
| FFT value (to satisfy the customer) | |
| Lifespan reaches 150,000 to 160,000 years | |
| Customer feedback | When using our metal CBN segment to process workpieces, there are large scratches on the surface and the tiles are obviously used and half of them are not used.
|
| Solutions | This extrusion mark wasn’t present at first, but began to appear after six or seven pieces.
Suggests the customer didn’t smooth the surface initially. Furthermore, the feed rate was too high. This is because the grit size is much finer than the customer’s previous experience, so the feed rate shouldn’t be too high. Furthermore, the photos show that some pieces are only halfway ground, further indicating the need for further finishing. The current solution is to have the customer smooth the surface and reduce the feed rate. |