Application of CBN Superfinishing Oilstones in Bearing Raceways
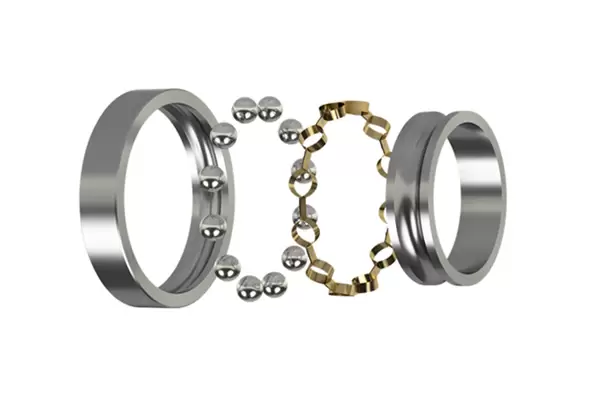
Bearing raceways are among the most critical surfaces in rotating machinery. Their geometric accuracy and surface integrity directly affect bearing life, vibration, noise, and the reliability of the entire machine. As bearing designs demand ever-higher speeds, smaller clearances, and better fatigue life, finishing technologies must deliver ultra-smooth surfaces with minimal subsurface damage. Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) superfinishing oilstones have emerged as a highly effective tool for achieving the required microfinish, dimensional accuracy and consistency on bearing raceways — both inner and outer rings.
In the manufacturing of rolling bearings, superfinishing, as the final process in ring processing, directly affects the vibration noise, fatigue life, and assembly quality of bearings. Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) superfinishing oilstones, as an advanced grinding tool, have unique advantages in bearing raceway processing and are gradually being widely used.
Why CBN for Bearing Raceways?
CBN is an advanced superabrasive second only to diamond in hardness for many applications, but it offers distinct advantages for finishing ferrous materials (steels and many bearing alloys):
* Thermal and Chemical Stability: Unlike diamond, CBN is stable when grinding steels (diamond reacts with iron at elevated temperatures). CBN therefore maintains cutting edges longer and resists graphitization or chemical wear.
* Consistent Cutting Action: CBN grains are sharp and friable in controlled ways that produce stable micro-cutting and produce surface finishes with low roughness and predictable textures.
* High Thermal Conductivity: Helps dissipate heat at the contact zone, reducing thermal damage to raceways and allowing for higher material removal rates during finishing strokes.
* Long Tool Life: Especially when bonded appropriately (vitrified, resin, or metal bonds), CBN oilstones maintain geometry and can be dressed to reuse, reducing per-part finishing cost.
These properties make CBN oilstones particularly well-suited for the final finishing of bearing raceways where micro-scale surface topology, metallurgical integrity and repeatability are essential.
What Is a CBN Superfinishing Oilstone?
A CBN superfinishing oilstone is a wheel or stone used in superfinishing (also called microfinishing or fine finishing) operations. It differs from conventional grinding wheels by having:
* Fine grit CBN grains (commonly in ranges such as 0.3–1.5 µm equivalents depending on manufacturer grading).
* A bond system (vitrified, resin or metal) optimized to expose and release grains progressively for controlled micro-cutting.
* High porosity or engineered pores to carry lubricant (oil) and assist chip evacuation.
* Low contact pressure operation; superfinishing relies on low-pressure, high-frequency stroking to produce surface improvement, not heavy material removal.
In bearing raceway finishing, these oilstones are applied with light normal forces, slow infeed, and controlled reciprocating/rotational motion to obtain Ra values in the single-digit nanometer range (or sub-0.1 µm average roughness) and favorable isotropic microtextures.
Key Requirements for Bearing Raceway Surfaces
Before choosing or applying CBN oilstones, understand what the raceway needs:
* Surface roughness: Target Ra often ranges from 0.02 to 0.2 µm for high-performance bearings; lower roughness reduces friction and wear.
* Microtexture: Directional textures or cross-hatch patterns influence lubricant film formation and fatigue initiation. Superfinishing should achieve an ideal surface lay.
* Dimensional tolerance & roundness: Final raceway form tolerance, concentricity and roundness must be maintained, typically in the low microns.
* Subsurface integrity: No grinding burns, tensile residual stresses or microcracks—these shorten fatigue life.
* Bore/OD fit: Finish must not significantly alter bearing fit; material removal is minimal but controlled.
CBN oilstones are effective because they remove microscopic peaks (asperities) and leave a compressive or neutral subsurface state when correctly applied.
Stone Selection: Bond, Grit and Grade
Selecting the right CBN oilstone requires balancing finish, removal rate and tool life:
* Grit size: Finer grains produce smoother finishes but lower removal rates. For final raceway finishing, very fine grits are common.
* Bond type:
—Vitrified bonds offer rigidity and excellent form retention — suitable for precision profile finishing.
—Resin bonds are more forgiving, provide higher stock removal initially, and often used when some microstock removal is needed before final passes.
—Metal bonds provide durability in heavy-duty operations.
* Porosity and structure: Engineered porosity helps oil retention and chip clearance — desirable in oilstone superfinishing.
* Grade (hardness): Softer bonds expose grains faster, producing consistent cutting action but may wear faster. Harder bonds last longer but can glaze — requiring dressing.
* Wheel geometry: Stone width, diameter and profile must match the raceway curvature and the machine’s stroke.
Manufacturers often provide selection charts for steel grades (e.g., 52100 bearing steel, through-hardened or case-hardened steels) linking steel hardness to recommended CBN grade and bond.
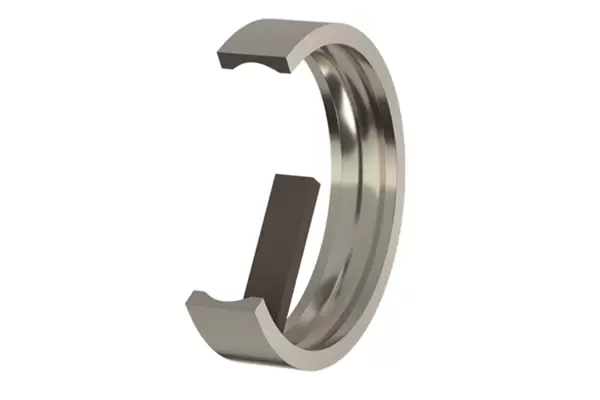
Features of CBN oil stone stone:
Specifically designed for the superfinishing of inner and outer raceways of bearings, it is suitable for both primary superfinishing (rough grinding) and secondary superfinishing (mirror polishing), significantly improving the surface finish and roundness accuracy of the raceways. For example, after using this oilstone for superfinishing, the surface finish of the raceway can be much smoother, and the roundness error can be effectively controlled within a very small range, which is crucial for the stable operation of bearings.
CBN oil stone has excellent properties such as good elasticity, strong cutting force, and high wear – resistance. The good elasticity allows the oilstone to adapt to the shape of the raceway better during the grinding process, ensuring uniform grinding. The strong cutting force enables efficient material removal, and the high wear – resistance ensures a long service life of the oilstone, reducing the frequency of replacement and improving production efficiency.
Grinding Materials
It is suitable for the honing of cylinder liners, cylinder liner seats, and connecting rods made of different materials (various cast irons, ceramics, aluminum alloys, and chrome – plated materials). It is widely used in industries such as automotive, motorcycle, refrigeration, bearings, shipbuilding, and aviation. For instance, in the automotive industry, it can be used to process engine cylinder liners, improving the performance and durability of the engine.
Principle
The oilstone with fine – grained abrasives is pressed against the workpiece surface under low – pressure and elastic conditions. The workpiece rotates, while the oilstone makes rapid reciprocating swings in a certain pattern perpendicular to the rotation direction of the workpiece. At the same time, good lubrication and cooling conditions are provided to reduce the surface roughness of the workpiece and improve the geometric accuracy. With domestic equipment, the surface roughness Ra of the processed surface can reach about 0.1μm, and with imported equipment, it can reach Ra 0.04μm or even lower.
Processing Technology
The processing of bearing raceways usually follows the process route of turning → heat treatment → grinding → superfinishing, where superfinishing is the key process. Turning is used to initially shape the raceway, heat treatment improves the hardness and mechanical properties of the material, grinding further refines the shape and size, and superfinishing finally achieves the high – precision surface quality required for the bearing raceway.
—EDITOR: Doris Hu
–POST: Doris Hu